Retail and consumer staples, for example, have relatively small asset bases but have high sales volume—thus, they have the highest average asset turnover ratio. Conversely, firms in sectors such as utilities and real estate have large asset bases and low asset turnover. An asset turnover ratio equal to one means the net sales of a company for a specific period are equal to the average assets for that period. The company generates $1 of sales for every dollar the firm carries in assets. Asset turnover ratio results that are higher indicate a company is better at moving products to generate revenue.
What Is the Main Downside to the Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio?
- The asset turnover ratio is a valuable financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in using its assets to generate revenue.
- Also, they might have overestimated the demand for their product and overinvested in machines to produce the products.
- It is important to consider the larger context in which your company operates to gain a more accurate understanding of the factors impacting your ratio.
- A higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a company has effectively used investments in fixed assets to generate sales.
This metric is also used to analyze companies that invest heavily in PP&E or long-term assets, such as the manufacturing industry. The fixed asset turnover (FAT) is one of the efficiency ratios that can help you assess a company’s operational efficiency. This metric analyzes a company’s ability to generate sales through fixed assets, also known as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Another effective strategy to improve your fixed asset turnover ratio is to regularly assess the condition and performance of your fixed assets. This can help you identify any assets that may be underutilized or in need of repair or replacement. By addressing these issues, you can improve the overall global trade finance program efficiency and productivity of your operations, which can lead to a higher fixed asset turnover ratio and increased profitability. Industry standards for the fixed asset turnover ratio can vary widely depending on the nature of the business, the industry, and the company’s competitive position.
Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio vs. Asset Turnover Ratio
Remember we always use the net PPL by subtracting the depreciation from gross PPL. Since using the gross equipment values would be misleading, we always use the net asset value that’s reported on the balance sheet by subtracting the accumulated depreciation from the gross. They measure the return on their purchases using more detailed and specific information. If the Fixed Asset Turnover for your company is low, it is not necessarily bad. Thomas J Catalano is a CFP and Registered Investment Adviser with the state of South Carolina, where he launched his own financial advisory firm in 2018.
While investors may use the asset turnover ratio to compare similar stocks, the metric does not provide all of the details that would be helpful for stock analysis. A company’s asset turnover ratio in any single year may differ substantially from previous or subsequent years. Investors should review the trend in the asset turnover ratio over time to determine whether asset usage is improving or deteriorating. The asset turnover ratio can vary widely from one industry to the next, so comparing the ratios of different sectors like a retail company with a telecommunications company would not be productive. Comparisons are only meaningful when they are made for different companies within the same sector. The asset turnover ratio tends to be higher for companies in certain sectors than others.
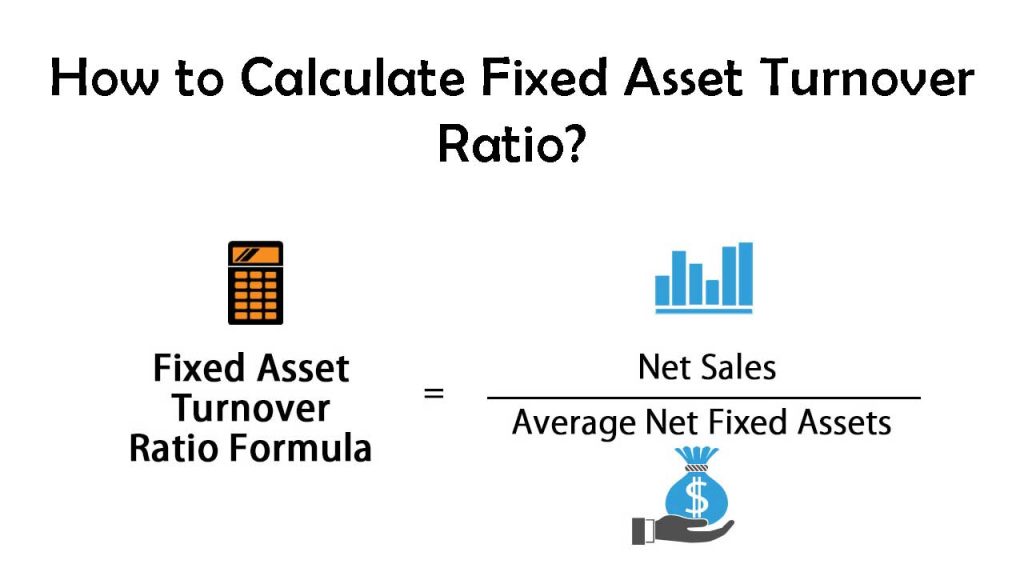
Formula
In other words, it shows how effectively a company is deploying its fixed assets to generate income. The asset turnover ratio measures how effectively a company uses its assets to generate revenues or sales. The ratio compares the dollar amount of sales or revenues to the company’s total assets to measure the efficiency of the company’s operations. To calculate the ratio, divide net sales or revenues by average total assets.
Moreover, the company has three types of current assets—cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory—with the following carrying values recorded on the balance sheet. As such, there needs to be a thorough financial statement analysis to determine true company performance. Yes, it could indicate underinvestment in fixed assets, which might lead to future capacity issues or inability to meet demand. The FAT ratio is one of many metrics that you, as an investor or business, can use to analyze the operational efficiency of a business. Companies with fewer assets on their balance sheet (e.g., software companies) tend to have higher ratios than companies with business models that require significant spending on assets.
For example, retail companies have high sales and low assets, hence will have a high total asset turnover. On the other hand, Telecommunications, Media & Technology (TMT) may have a low total asset turnover due to their high asset base. Thus, it is important to compare the total asset turnover against a company’s peers. Check out our debt to asset ratio calculator and fixed asset turnover ratio calculator to understand more on this topic.